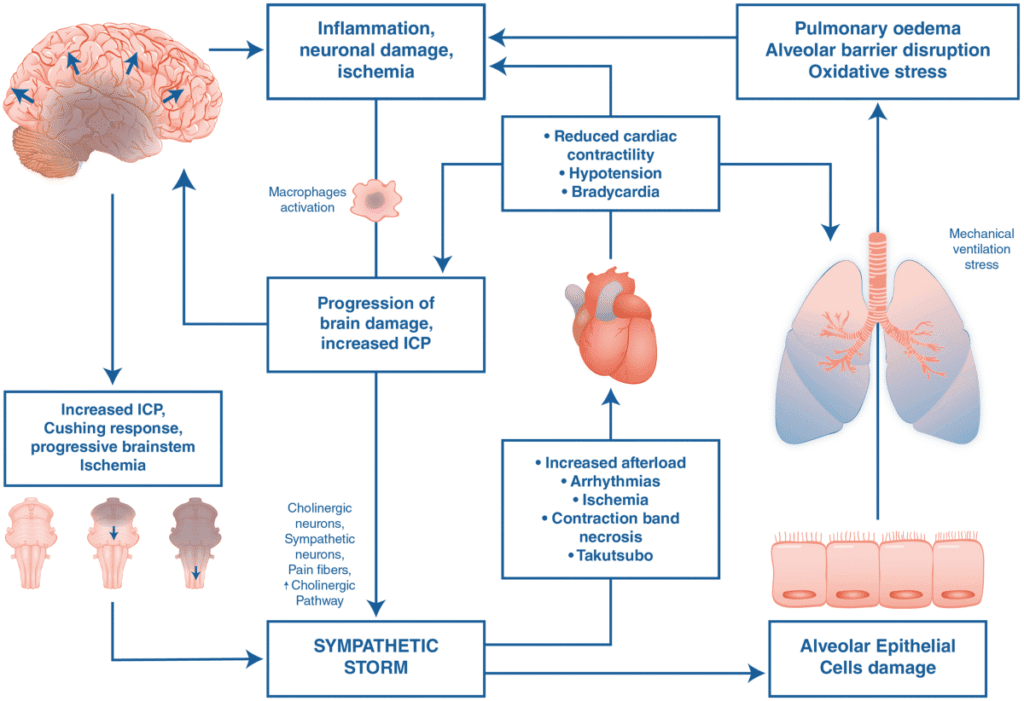
Comprehensive Management Approach
1. Temperature Management
Primarily, prevent hypothermia (<34°C). Therefore, target core temperature >35.8°C.
Methods include:
- Warm blankets
- Fluid warmers
- Heated humidifiers
- Adjusted ambient temperature
2. Cardiovascular Management
Simultaneously, maintain normovolemia while optimizing cardiac output. Furthermore, control blood pressure and minimize the use of vasoactive agents. Additionally, maintain organ perfusion throughout.
3. Respiratory Management
Specifically, implement lung protective ventilation:
- Tidal volume: 6 ml/kg ideal body weight
- PEEP: 5-10 cmH₂O
- Peak pressure: <40 cmH₂O
- Plateau pressure: <35 cmH₂O
- Target SpO₂: >92%
- Target PaO₂: >70 mmHg
4. Endocrine Management
Concurrently, manage diabetes insipidus while providing thyroid hormone replacement. Additionally, provide corticosteroid support and manage insulin requirements.
Hemodynamic Targets
Medical teams should maintain these parameters:
| Parameter | Target Range | Monitoring Method |
| Heart Rate | 60-120 BPM | Continuous ECG |
| Blood Pressure | SBP >100, MAP >70 mmHg | Arterial line |
| Central Venous Pressure | 6-10 mmHg | CVP monitor |
| Urine Output | 0.5-3 ml/kg/hr | Hourly measurement |
| SpO₂ | >96% | Pulse oximetry |
| Cardiac Index | >2.4 L/min/m² | Thermodilution |
Pharmacological Support
Vasopressor Preferences:
First-line: Use vasopressin (beneficial for diabetes insipidus, doesn’t reduce organ blood flow)
Second-line: Administer norepinephrine (increases renal and coronary blood flow)
Avoid prolonged use: Minimize dopamine (depletes norepinephrine stores, affects post-transplant function)
Fluid Management:
Preferred: Use crystalloids with balanced salt (RL, 0.45% NS)
Avoid: Do not use 0.9% NS (hyperchloremic acidosis), 5% dextrose (hyperglycemia)
Colloids: Avoid HES (damages renal cells), consider albumin 4%/20% as acceptable
Hormone Replacement:
Specifically:
- Vasopressin: 20 U in 500 ml D5W, titrate based on urine output
- Levothyroxine: 150 μg daily IV
- Methylprednisolone: 200 mg in 100 ml NS, 4 ml/hr infusion
Monitoring Protocol
Continuous assessment requires:
- Vital signs: Every 1 hour
- Urine output: Hourly measurement
- Arterial blood pressure: Continuous monitoring
- ABG analysis: Every 6 hours
- Core temperature: Every 1 hour
Therapeutic Targets:
Maintain MAP >65 mmHg, ensure hemoglobin >10 g/dL. Additionally, keep sodium <160 mmol/L and potassium 3.5-5 mmol/L. Furthermore, target mixed venous oxygen saturation >70%, maintain blood glucose 140-180 mg/dL, and ensure central body temperature >36.0°C.
Required Investigations
Laboratory Tests:
Basic tests include: CBC, LFT with proteins, RFT, electrolytes, including Ca, Mg, PO4
Cardiac markers: Test troponin I, CPK-total, pro-BNP
Tumor markers: Screen for CEA, PSA, CA19-9, CA125, alpha-fetoprotein
Endocrine assessment: Evaluate T3, T4, TSH, HbA1c
Coagulation studies: Check PT, INR
Infection screening: Perform blood grouping, CRP, PCT, ESR
Infectious Disease Screening:
Comprehensively test for HIV, Hepatitis A/B/C, CMV, EBV, and syphilis. Additionally, obtain urine, blood, and sputum culture & sensitivity.
HLA Typing:
Specifically, perform HLA A, B, DR, DQ DNA typing and conduct HLA crossmatch compatibility testing.
Imaging Studies:
Routinely, obtain:
- Chest X-ray
- Hepatobiliary and kidney ultrasonogram
- Non-contrast CT abdomen and pelvis
- Non-contrast brain CT scan
General ICU Care
Standard care includes:
- Central line and arterial line insertion and monitoring
- Nasogastric tube insertion and care
- Temperature monitoring (nasal or rectal)
- Foley catheter management
- Head elevation 30°-40°
- Regular side-to-side positioning
- DVT prophylaxis with pneumatic compression
- Eye protection and frequent airway suctioning
- Ulcer prophylaxis and broad-spectrum antibiotics